A team led by Associate Professor CHNG has solved a 60-year-old mystery in bacterial cell envelope biology, defining the primary function of an important protein complex responsible for maintaining the stability of the outer membrane (OM). The team has made a significant breakthrough, and conclusively defined the primary function of the Tol-Pal complex in OM lipid homeostasis. Using an elegant genetic approach, the team engineered a variant of the Tol-Pal complex that was re-directed away from, and thus could not perform associated roles at the cell division site (where the bacterial cell constricts and eventually separates into daughter cells). Strikingly, this Tol-Pal variant was fully capable of maintaining OM lipid homeostasis, and thus OM stability and barrier function. The findings were published in the scientific journal Nature Communications.
Dr TAN Wee Boon, a senior research fellow in the Chng group and first author of the study said, “We have unambiguously established the true physiological function of the Tol-Pal complex, more than 60 years after its first discovery.” This new knowledge on the Tol-Pal complex sets the foundation for the development of future drugs that target OM lipid homeostasis to disrupt the OM barrier and/or kill the bacteria. “This breakthrough marks an important conceptual advance in our overall understanding of bacterial outer membrane assembly and lipid transport, and is a testament to our consistent efforts towards elucidating the fundamental mechanics of the living cell,” added Prof Chng. Read the full article here.
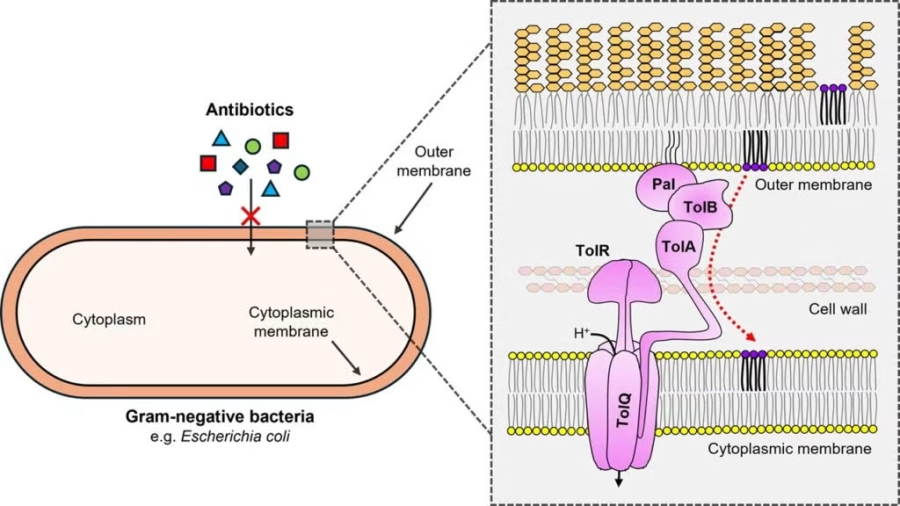
The Tol-Pal complex maintains bacterial outer membrane (OM) stability by regulating lipid homeostasis. (Left) In Gram-negative bacteria, the OM acts as a protective barrier, blocking entry of harmful substances like antibiotics. (Right) The Tol-Pal complex spans the cell envelope, using energy from the cytoplasmic membrane (in the form of a proton gradient) to drive lipid transport. This retrograde transport process retrieves excess phospholipids (purple) from the OM back to the cytoplasmic membrane, ensuring membrane balance and integrity.
