Research Fellow, Institute of Molecular and Cell Biology, 1994-1996; Research Fellow, The Scripps Research Institute, 1992-1994; Ph.D., National University of Singapore, 1992; B.Sc. (Hons), National University of Singapore, 1987.
Contact Information:
Office: S8-05-09
Tel: (65)-6516-2688
Fax: (65)-6779-1691
Email: chmlamyl@nus.edu.sg
Our research focuses on bioorganic and medicinal chemistry, specifically the synthesis and biological evaluation of novel organic compounds and natural product derivatives as potential therapeutic agents.
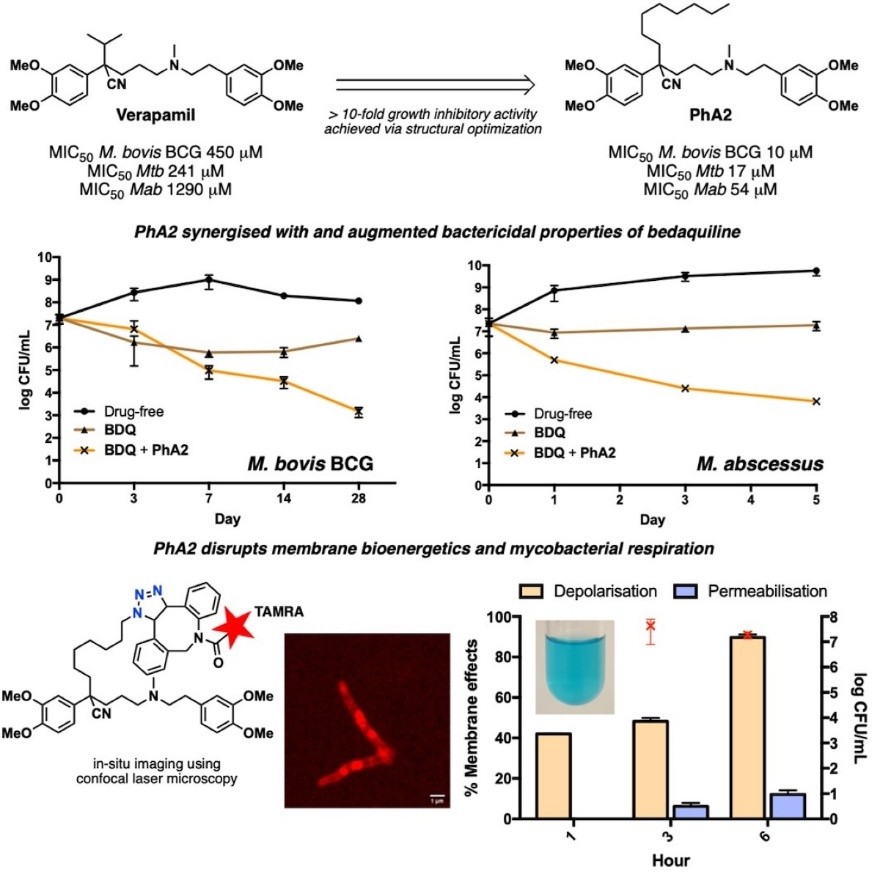
Ref: Clinically efficacious combination therapies capable of impeding resistance are widely sought for the treatment of mycobacterial infections. Here, we described structural modifications of the phenylalkylamine scaffold of verapamil to give an analog with more than 10-fold greater growth inhibitory activity than verapamil against Mycobacterium tuberculosis, M. bovis BCG, and M. abscessus abscessus (Mab abscessus). The analog synergized with the F1Fo-ATP synthase inhibitor bedaquiline in checkerboard assays and augmented the bactericidal properties of bedaquiline against M. bovis BCG and Mab abscessus. Using live cell bioorthogonal imaging techniques, in vitro biochemical and genetic assays, the bactericidal activity of the analog is attributed to the perturbation of membrane bioenergetics and disruption of mycobacterial respiration. Overall, its promising activity profile, mode of action and synergistic interaction with bedaquiline support further exploration of the phenylalkylamine scaffold as a valued source of potential leads for antimycobacterial drug discovery. (iScience 2025, 28, 112915, DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.112915)
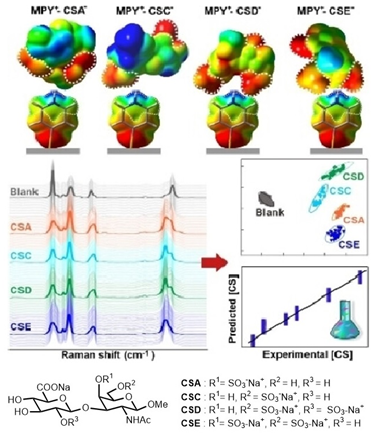
Ref: Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) regulate many important physiological processes. A pertinent issue to address is whether GAGs encode important functional information via introduction of position specific sulfate groups in the GAG structure. However, procurement of pure, homogenous GAG motifs to probe the “sulfation code” is a challenging task due to isolation difficulty and structural complexity. To this end, we devised a divergent synthetic strategy to obtain all the 16 theoretically possible sulfation patterns in the chondroitin sulfate (CS) repeating unit; these include rare but potentially important sulfated motifs which have not been isolated earlier.
Molecular recognition of different CS analogues is achieved via surface-enhanced Raman scattering spectroscopy and by inducing charge and geometry complementarity between 4-mercaptopyridine probe and the CS isomers. By “locking” each CS in a unique complex geometry via site-specific, multidentate interactions, our platform mimics molecular docking events to enable high spectral specificity and multiplex quantification. (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, e202309610).